
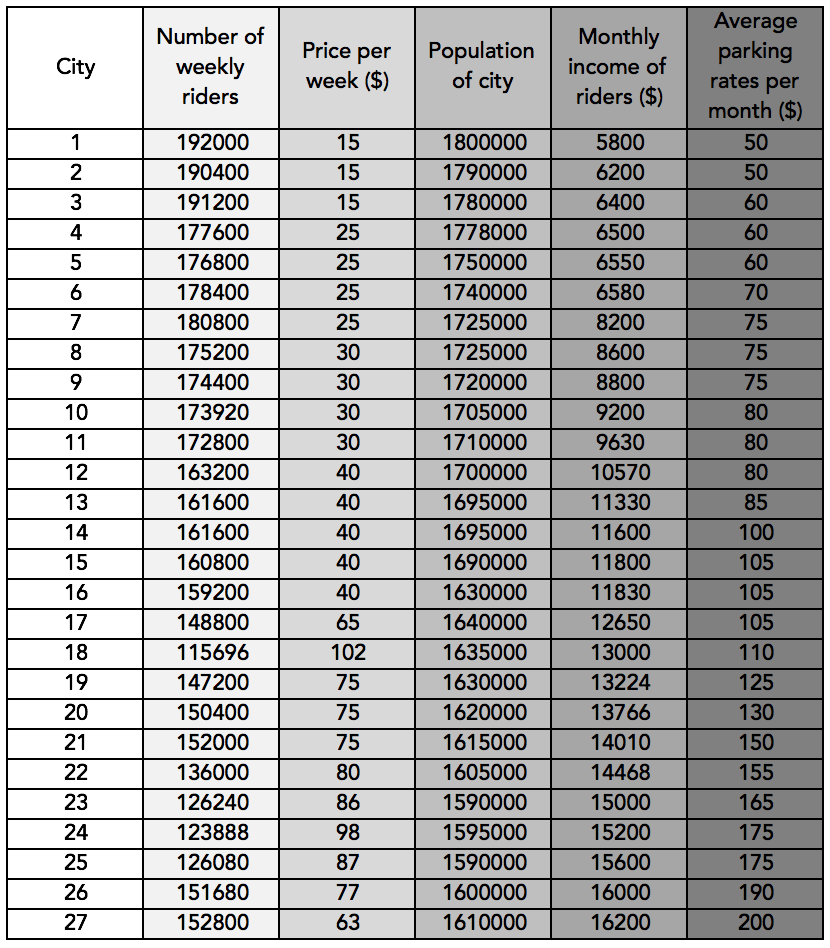
Excel can save files in 'comma delimited format', or. Data can be entered and edited using Excel. Data sets are arranged with each column representing a variable, and each row representing a subject a data set with 5 variables recorded on 50 subjects would be represented in an Excel file with 5 columns and 50 rows.
Results from analyses can also be saved as objects in R, allowing the user to manipulate results or use the results in further analyses.ĭata can be directly entered into R, but we will usually use MS Excel to create a data set.

For our basic applications, results of an analysis are displayed on the screen. For example, if 'cholesterol' was an object representing cholesterol levels from a sample, the function 'mean(cholesterol)' would calculate the mean cholesterol for the sample. Functions in R perform calculations on objects. For our basic applications, matrices representing data sets (where columns represent different variables and rows represent different subjects) and column vectors representing variables (one value for each subject in a sample) are objects in R. R is related to the S statistical language which is commercially available as S-PLUS. Check that you download the correct version of R for your operating system (for example, XP for the PC, Tiger or earlier versions of OSX for Macs).
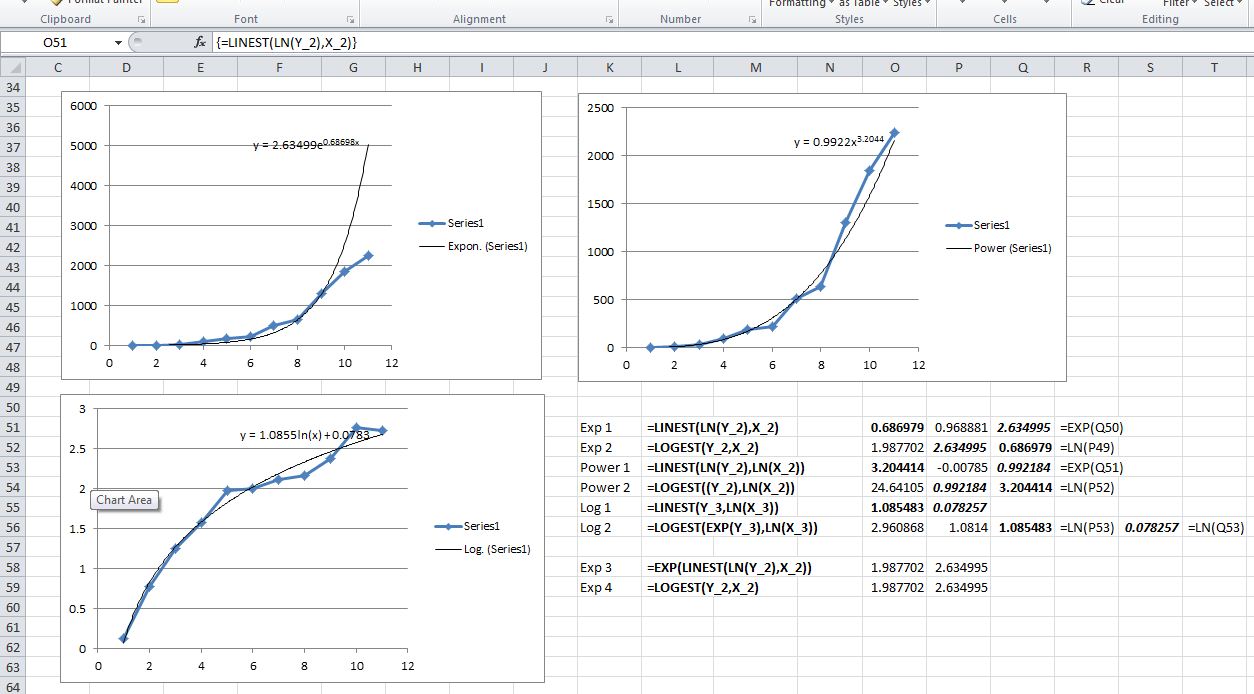
R can be downloaded from the Internet site of the Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN) (). R is a freely distributed software package for statistical analysis and graphics, developed and managed by the R Development Core Team. Milton, PhD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Biostatisticsīoston University School of Public Health Basic Statistical Analysis Using the R Statistical Package Introduction Other than that, I have not had to use any other quantity on the regression statistics table in my 7 University semesters.Basic Statistical Analysis Using the R Statistical Package The closer it is to #1#, the better it is, but it is only for a linear fit line. Oftentimes, even in a quantitative analysis course, you only need to further know the coefficient of determination #R^2#. Here is an example of an Ohm's law analysis I did using a similar regression statistics table: Where #s# is the standard deviation above, and: Where #N# is the number of trials, #x_i# is each individual value, and #barx# is the average of said values. Intercept Associated Error ( #AE_"int"#).The Associated Error is basically the uncertainty you have.įor example, in a standard physics lab course, bare minimum, here's what you would need to know: If you multiply the Standard Error by #1.96#, you get the Associated Error for either the Intercept or the Slope. "HH SIZE" refers to the Slope, and of course, Intercept is the y-intercept. The "Coefficients" are the slope or y-intercept in this case.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
